World Water Day (WWD), held every year on March 22 considering that 1993, is a United Nations observance to raise public awareness of water resource conservation.
Among its primary objectives is to support the accomplishments of Sustainable Development Goal 6: water and sanitation for all by 2030.
Each year, the UNs coordination system on water and sanitation, UN-Water, identifies the theme for WWD.
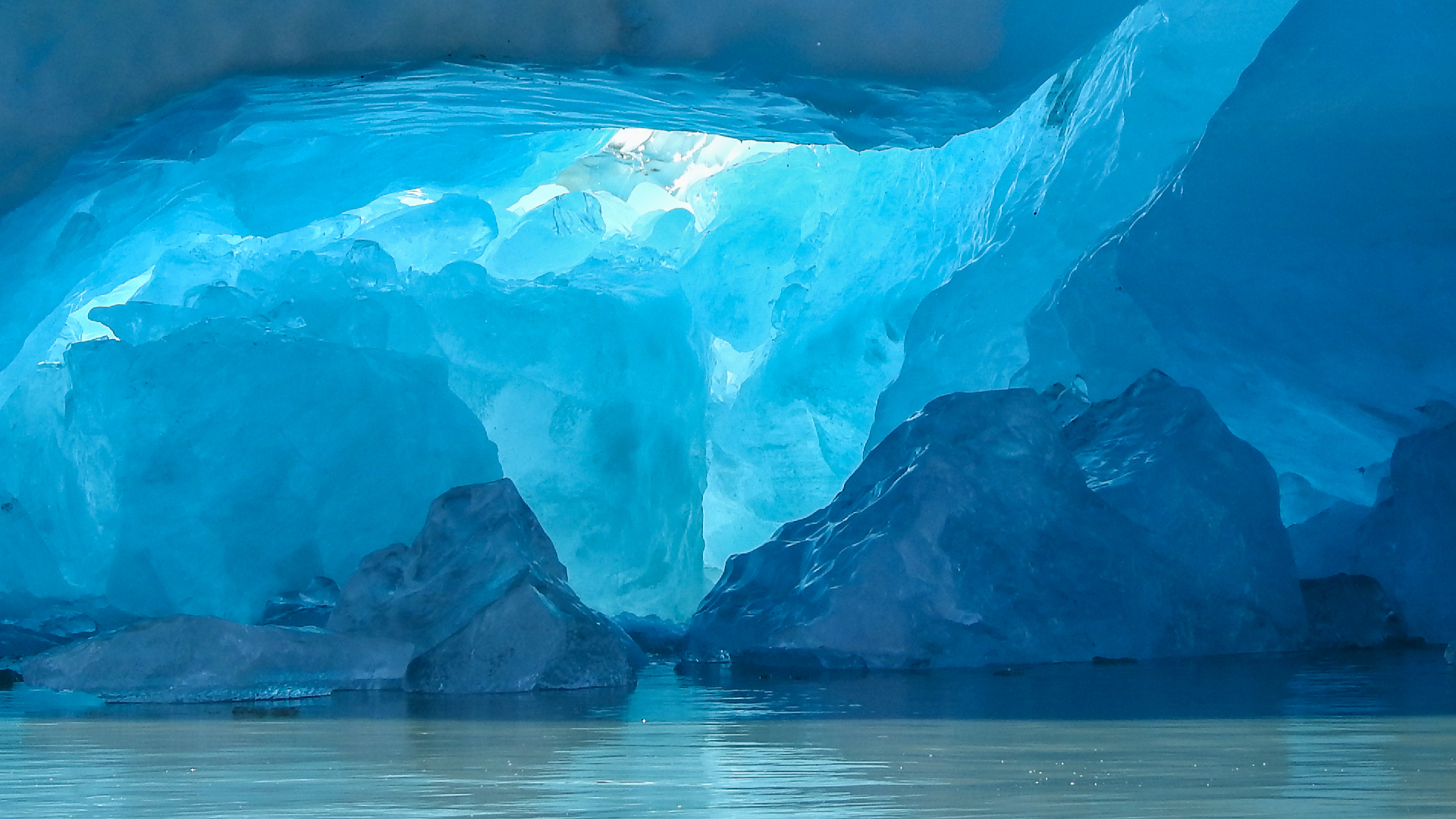
This year marks the 33rd WWD, and the theme is Glacier Preservation.
Glaciers are masses of ice formed from collected snow that are capable of movement.
In high-latitude and high-altitude regions, when snow collects and remains year-round without melting, it goes through a series of physical improvements to become ice.
Once the ice reaches a particular thickness, it starts to move under the impact of gravity and its own weight, thus forming a glacier.According to China Media Group, 71 percent of the Earths surface area is covered by water, only 2.5 percent is freshwater.
Of this freshwater, less than 0.3 percent is really usable.
Besides, around 2.7 billion individuals worldwide are confronted with serious water scarcity.Approximately 70 percent of the Earths freshwater exists as snow or ice.
2 billion people depend on natural tanks for freshwater resources from melting glaciers, according to the UN WWD Report released March 21.
However, glaciers around the world have actually remained in a general state of retreat considering that the mid-19th century.
The years 2022 to 2024 have seen the largest glacier mass losses on record, according to the World Meteorological Organization.The total location of glaciers in China was around 46,000 square kilometers, with about 69,000 specific glaciers around 2020.
Compared to the First Chinese Glacier Inventory, the glacier location in China reduced by about 26% from the 1960s to 2020, at a rate of 4.8% per decade.
Throughout this duration, around 7,000 small glaciers vanished totally, according to the Third Chinese Glacier Inventory launched on Friday.The primary causes of glacier melting are diverse.
Worldwide warming, which leads to increasing temperatures, is a major driver that speeds up the melting of glaciers.
Seasonal variations likewise play a significant role, as higher temperatures in summer season accelerate the melting process, while decreased snow accumulation in winter season results in an imbalance of glacier mass.
Additionally, the deposition of black carbon from air toxins reduces the reflectivity of the ice surface, more accelerating the melting of snow and ice.The melting of glaciers has a series of significant effects.
The increase of meltwater into the oceans adds to increasing sea levels, posturing a threat to seaside neighborhoods and ecosystems.
While this process initially increases river flow, it might ultimately cause a scarcity of freshwater resources.
In addition, the retreat of glaciers interrupts habitats, threatening the survival of numerous plant and animal species.
Glacier melting can exacerbate severe weather events, consisting of floods and droughts.The UN WWD Report stressed that there is an urgent requirement to substantially lower carbon emissions.
China has likewise been actively taken part in securing water resources.The 38th China Water Week occurs from March 22 to 28.
Regions throughout the country are hosting a diverse selection of activities to raise public awareness of water conservation and defense.(Cover through VCG)

 17
17